Financial Inclusion in Nigeria
Financial inclusion in Nigeria means making sure that everyone – whether rich or poor, living in the city or village – can access and use basic financial services like bank accounts, savings, loans, and insurance. It’s about ensuring that these services are affordable, easy to use, and available to all Nigerians.
Financial inclusion helps people and businesses manage their money better, plan for the future, and protect themselves from unexpected financial problems.
Importance of Financial Inclusion in Nigeria
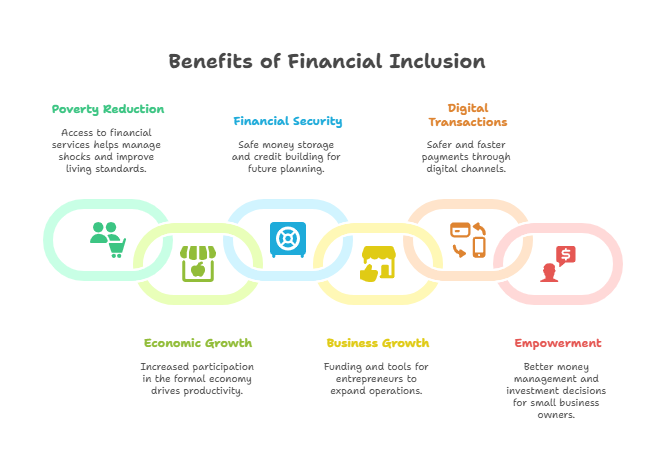
Financial inclusion is important in Nigeria for several reasons:
- It reduces poverty.
- It boosts economic growth.
- It improves financial security.
- It encourages the growth of business.
- It promotes digital and cashless transactions
- It empowers small business owners to improve financial stability.
Statistics and Trends in Financial Inclusion in Nigeria
Financial inclusion in Nigeria has experienced big progress in recent years, thanks to growing financial literacy, increased use of digital financial services, and expanding financial technology (fintech) solutions.
However, there are still challenges in achieving these ambitious targets. Below is a quick overview of key statistics and recent trends and development of financial inclusion in Nigeria.
Key Statistics
-
Overall Financial Inclusion:
As of 2023, about 74% of Nigerian Adults had access to financial services, this reflects steady progress toward the National Financial Inclusion Strategy target of 95% inclusion by 2024. This means that nearly three out of every four Nigerians can now access banking, savings, and payment services, which is a big step to financial stability.
-
Formal Financial Inclusion:
The percentage of Nigerians using formal financial services increased from 56% in 2020 to 64% in 2023. This growth is caused mostly by mobile banking, digital wallets, and fintech innovations that make financial services more accessible.
-
Financial Exclusion Rate:
Despite the progress, 26% of Nigerian Adults still don't have anything to do with financial services, this was caused due to limited access to banks in rural areas and low financial literacy level.
Financial technology trends in Nigeria
-
Fintech Growth and Digital Innovation:
Fintech companies are driving financial inclusion in Nigeria by making mobile banking and payment platforms easy to use. Mobile apps and digital wallets have made it easier for people, even in rural areas, to send and receive money, pay bills, and access loans without having to use a traditional bank. Additionally, for those looking to grow their wealth, using one of the 10 best investment apps for beginners can be a great way to start investing.
-
Financial Literacy and Education:
To improve financial literacy in Nigeria is becoming a national priority. In November 2024, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) launched a campaign to educate Nigerians about managing money, using credit wisely and also investing.
More Nigerians are beginning to understand how to save, budget, and invest, this is helping them to make better financial decisions. Learning how to make money online in Nigeria is also becoming an essential part of financial literacy, empowering individuals with new income opportunities.
-
Local Currency Financing:
In October 2024, the Central Bank of Nigeria partnered with the International Finance Corporation (IFC) to increase naira-based financing for small businesses. This move will help businesses avoid foreign exchange risks and make borrowing easier and more affordable.
-
Rise of Mobile and Cashless Transactions:
The use of mobile money and digital payment systems is growing very fast! Services like Paga, Opay, and Palmpay have made it easier for Nigerians to conduct cashless transactions, even in rural areas like villages too. In fact, mobile money grew by 35% in 2023 alone.
Government policies and fintech solutions
Financial inclusion in Nigeria has improved in recent years because of strong support from the government and venture capital investments in financial industries, which in turn has helped in giving access to financial services in Nigeria.
The government ‘s policies aim to make financial services available to everyone, especially those in rural areas and low-income groups.
-
Role of Government in Financial Inclusion
The Nigerian government has introduced several policies to make people have access to financial services, especially those without bank accounts or don’t have easy access to banks.
-
National Financial Inclusion Strategy (NFIS):
In 2012, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) introduced the National Financial Inclusion Strategy to reduce the number of people without access to financial services in Nigeria. This strategy has helped more people to open bank accounts, use mobile banking, and access credit.
-
Credit Access Expansion:
In January 2025, the Nigerian government announced the creation of a National Guarantee Company to help small businesses and individuals get loans more easily. This will make it easier for traders, farmers, and small business owners to grow their businesses.
-
Financial Literacy Campaigns:
The CBN also introduced programs to teach Nigerians how to manage their money better. In November 2024, the CBN held community events to educate people about saving, borrowing, and using digital banking services. As part of this effort, financial education is also being integrated into schools through initiatives like the Back to School Project.
-
Fintech Solutions Driving Financial Inclusion
Fintech companies have made financial services easier to use and more accessible to people who don’t have bank accounts or live far from banks.
-
Mobile Money and Digital Wallets:
Fintech companies like Paga, Opay, and Palmpay allow people to send and receive money, pay hills, and access loans using their phones.
-
Moniepoint’s Success:
In October 2024, Nigerian fintech company Moniepoint became a big fish after raising $110 million in funding. Moniepoint helps small businesses accept cashless payments and provides loans to business owners.
-
Agent Banking(POS):
Fintech companies have partnered with banks to expand agent banking. These agents help people open accounts, deposit, and withdraw money, even in rural communities without banks. By 2023, over 1.5 million agents were working across Nigeria.
-
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency:
Some fintech companies are using blockchain technology to make cross-border payments cheaper and also fast. This is helping Nigerians that are working abroad to send money back home more easily.
-
Microloans and Peer-to-peer Lending:
Platforms like Carbon and Fairmoney offer small loans to people and businesses without needing collateral. Guess what? The loans are approved quickly using smartphone apps, helping traders and farmers grow their business.
-
Why Government and Fintech Collaboration Matters
The partnership between the Nigerian government and fintech companies is helping more Nigerians access financial services.
- Government policies are encouraging more bans and financial institutions to create products for low-income groups.
- Fintech companies are making it easier for people to access these services using mobile phones and digital platforms.
- Financial literacy programs are helping Nigerians understand how to manage their money and use financial services more effectively.
Challenges and Barriers to financial inclusion
Despite progress in financial inclusion in Nigeria, many people still face difficulties in accessing and using financial services, issues like poor infrastructure, low financial literacy, and lack of trust in financial institutions.
Understanding these challenges is key to improving access to financial services and increasing the number of banked Nigerians.
-
Poor Access to Financial Services
- Many rural communities don’t have banks or ATMs, so withdrawing money or opening accounts is difficult.
- Poor internet makes it difficult to use mobile banking and digital wallets.
- Some financial services charge high fees, discouraging them from using them.
-
Low Financial Literacy
- Many Nigerians don't understand how to manage money, save, or access credit.
- Some people are hesitant to use mobile banking apps because they don’t know how they work.
- Some people are scared about scams and security, so they avoid financial services.
-
Lack of Trust in Financial Institutions
- Past bank failures have made some Nigerians distrust financial institutions.
- Most times, poor customer service discourages people from using them.
- Banking rules and government policies changing every time can make the people reluctant from using these financial services.
-
Economic Challenges
- People with unstable incomes find it hard to save or meet up with loan requirements.
- Rising prices reduce the value of savings and make it difficult for people to plan or invest for the future.
- Without steady jobs, many Nigerians may lack the financial stability needed to access formal financial services.
Future Outlook and Recommendations for Financial Inclusion In Nigeria
Nigeria has made significant progress in expanding financial inclusion, but more work is needed to reach other populations and ensure that everyone benefits from financial services. The rise of mobile money and digital banking has created new opportunities to improve financial access.
Strengthening financial inclusion can have a significant impact on Nigeria’s economy by boosting economic growth, increasing investments, and reducing poverty.
Future Outlook
The future of financial inclusion in Nigeria looks promising, especially with the growing influence of mobile technology and digital platforms.
-
Growth of Mobile Money
- Mobile money services like Paga, Opay, and Palmpay have made it easier to send and receive money, pay bills, and access loans without visiting a bank.
- By 2026, mobile money is expected to account for over 60% of financial transactions in Nigeria according to Africa Financial Review, 2024.
- More rural communities are gaining access to mobile money through agent banking and expanding mobile networks, helping to bank the unbanked in Nigeria.
-
Rise of Digital Banking
- Digital banking platforms like Kuda, are attracting younger Nigerians with no-fee accounts, fast loans, and user-friendly apps.
- The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) is expected to introduce new guidelines to support digital banking growth and improve financial security.
-
Economic Impact of Financial Inclusion
- Increased financial inclusion will surely help small businesses grow by giving them access to loans and payment solutions.
- More Nigerians using banking services will lead to higher savings rates and more investments in the local economy.
- A stronger financial system will surely bring foreign investments and create more jobs, this will reduce poverty and make life better.
Recommendations
To improve financial inclusion in Nigeria, the government, financial institutions, and fintech companies need to work together to remove existing barriers and create more inclusive financial services.
- Increase mobile money in rural communities.
- Lower transaction fees to make services affordable.
- Improve mobile network coverage for better service access.
- Introduce financial education in schools and communities.
- Run media campaigns to raise awareness about saving and investing.
- Encourage banks to create user-friendly, low-cost digital platforms.
- Develop fintech solutions that are suited for low-income groups and small businesses.
- Strengthen partnerships between fintech and traditional banks.
- Improve customer protection laws to prevent frauds.
- Make account opening easier by making the ID and requirements simple.
- Ensure fintech platforms are security conscious.
FAQs
-
How do we improve financial inclusions in Nigeria?
- Expand mobile money and agent banking to rural communities.
- Lower financial costs and simplify account opening processes.
- Increase financial literacy through schools and community programs.
- Strengthen consumer protection to build trust in financial services.
-
What are the best fintech companies driving financial inclusions in Nigeria?
- Paga – Mobile payments and agent banking network.
- Kuda – Free digital banking with quick loans.
- Opay – Mobile-based payments and transfers.
- Fairmoney – Instant, collateral-free loans through a mobile app.
- Moniepoint – Business payments and small business loans.
-
How do Microfinance banks influence financial inclusion in Nigeria?
- They provide small loans and savings accounts to low-income earners.
- They offer financial education to improve money management skills.
- They support small businesses with credit and financial advisory services.
-
What is the role of digital banking in Nigeria's financial sector?
- Increases access to financial services through mobile apps and online platforms.
- Offers fee-free accounts, fast transfers, and quick loans.
- Encourages cashless transactions, boosting economic growth.
-
What are the financial inclusion success stories in Nigeria?
- Paga – Over 20 million users and $10 billion in transactions.
- Kuda – Over 7 million users with no-fee banking.
- Moniepoint– Processes over $100 billion annually for small businesses.
- AfriGo – Nigeria’s first domestic payment card, increasing local access.
- Fairmoney– Over $1 billion in loans through fast mobile approvals.
Conclusion
Financial inclusion in Nigeria is improving through mobile money, digital banking, and targeted government policies. Platforms like Paga, Kuda, and Opay are helping to bank the unbanked and provide quick, affordable financial services.
Expanding financial literacy, improving internet access, and reducing transaction fees will also help to drive inclusion. With these support and innovation still intact and improving, Nigeria’s financial sector can become more accessible and inclusive for all of us.